Spring Framework 5基础-简单例子引入
本文最后更新于:6 天前
设计一个Spring的Hello World
结合上面的使用场景,设计一个查询用户的案例的两个需求,来看Spring框架帮我们简化了什么开发工作:
- 查询用户数据 - 来看DAO+POJO-> Service 的初始化和装载。
- 给所有Service的查询方法记录日志
引入Spring框架的POM依赖,以及查看这些依赖之间的关系
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>tech.pdai</groupId>
<artifactId>001-spring-framework-demo-helloworld-xml</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<spring.version>5.3.9</spring.version>
<aspectjweaver.version>1.9.6</aspectjweaver.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${aspectjweaver.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>POJO - User
POJO是Plain OrdinaryJava Object的缩写,但是它通指没有使用Entity Beans的普通java对象,可以把POJO作为支持业务逻辑的协助类。
package org.books.tanzicai.entity;
/**
* @author tanzicai
*/
public class User {
/**
* user's name.
*/
private String name;
/**
* user's age.
*/
private int age;
/**
* init
* @param name user'name
* @param age user's age
*/
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}DAO 获取 POJO, UserDaoServiceImpl (mock 数据)
DAO(Data Access Object)顾名思义是一个为数据库或其他持久化机制提供了抽象接口的对象,在不暴露底层持久化方案实现细节的前提下提供了各种数据访问操作。
Mock 数据是前端开发过程中必不可少的一环,是分离前后端开发的关键链路。通过预先跟服务器端约定好的接口,模拟请求数据甚至逻辑,能够让前端开发独立自主,不会被服务端的开发所阻塞。
package org.books.tanzicai.dao;
import org.books.tanzicai.entity.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author tanzicai
*/
public class UserDaoImpl {
/**
* init
*/
public UserDaoImpl () {
}
/**
* mocked to find user list
* @return user list
*/
public List<User> findUserList() {
return Collections.singletonList(new User("pdai", 18));
}
}增加XML配置daos.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="org.books.tanzicai.dao.UserDaoImpl">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for data access objects go here -->
</beans>
业务层 UserServiceImpl(调用DAO层)
业务层:实现主要的业务需求
package org.books.tanzicai.service;
import org.books.tanzicai.entity.User;
import org.books.tanzicai.dao.UserDaoImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author tanzicai
*/
public class UserServiceImpl {
/**
* user dao impl
*/
private UserDaoImpl userDao;
/**
* init
*/
public UserServiceImpl() {
}
/**
* find user list
* @return user list
*/
public List<User> findUserList() {
return this.userDao.findUserList();
}
/**
* set dao
* @param userDao user dao
*/
public void setUserDao(UserDaoImpl userDao){
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}并增加services.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- services -->
<bean id="userService" class="org.books.tanzicai.service.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="org.books.tanzicai.dao.UserDaoImpl"/>
<!-- more bean definitions for services go here -->
</beans>
日志记录
使用Aspect切面编程拦截所有service中的方法,并输出记录
package org.books.tanzicai.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author tanzicai
*/
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
/**
* aspect for every methods under service package.
*/
@Around("execution(* org.books.tanzicai.service.*.*(..))")
public Object businessService(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// get attribute through annotation
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
System.out.println("execute method: " + method.getName());
// continue to process
return pjp.proceed();
}
}并增加aspects.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.books.tanzicai" />
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="logAspect" class="org.books.tanzicai.aspect.LogAspect">
<!-- configure properties of aspect here as normal -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for data access objects go here -->
</beans>
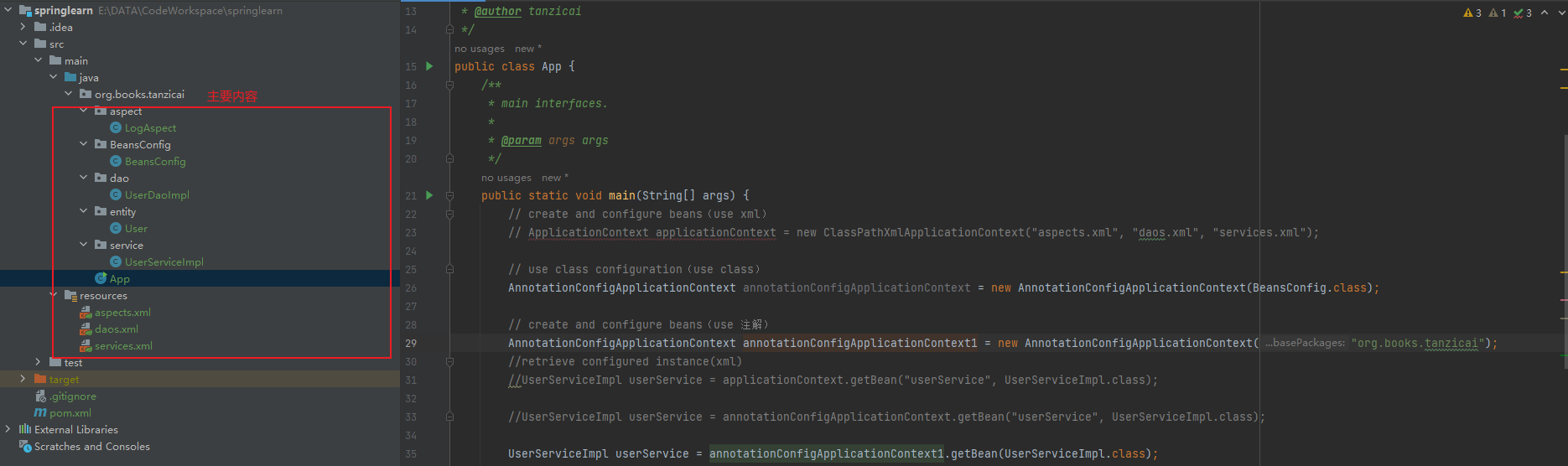
组装App
package org.books.tanzicai;
import org.books.tanzicai.BeansConfig.BeansConfig;
import org.books.tanzicai.entity.User;
import org.books.tanzicai.service.UserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author tanzicai
*/
public class App {
/**
* main interfaces.
*
* @param args args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create and configure beans(use xml)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aspects.xml", "daos.xml", "services.xml");
//retrieve configured instance(xml)
UserServiceImpl userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserServiceImpl.class);
//use configured instance
List<User> userList = userService.findUserList();
// print info from beans
userList.forEach(a-> System.out.println(a.getName()+","+a.getAge()));
}
}
解读
需求一
看第一个需求:查询用户(service通过调用dao查询pojo),本质上如何创建User/Dao/Service等;
没有Spring框架的话,我们的创建User/Dao/Service
UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
UserSericeImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
userService.setUserDao(userDao);
List<User> userList = userService.findUserList();有了Spring框架,可以将原有Bean的创建工作转给框架, 需要用时从Bean的容器中获取即可,这样便简化了开发工作,Bean的创建和使用分离了。
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aspects.xml", "daos.xml", "services.xml");
// retrieve configured instance
UserServiceImpl service = context.getBean("userService", UserServiceImpl.class);
// use configured instance
List<User> userList = service.findUserList();- SpringFramework通过xml配置创建对象
- 创建的对象可以从IoC Container中获取到
- 然后通过获取到的对象执行相应的方法
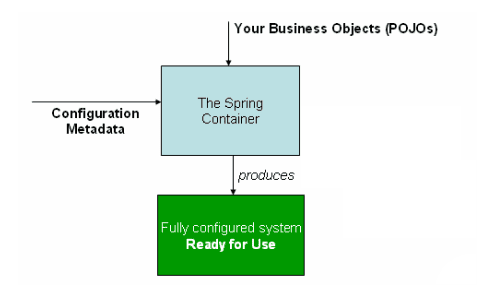
更进一步,你便能理解为何会有如下的知识点了:
- Spring框架管理这些Bean的创建工作,即由用户管理Bean转变为框架管理Bean,这个就叫控制反转 - Inversion of Control (IoC)
- Spring 框架托管创建的Bean放在哪里呢? 这便是IoC Container;
- Spring 框架为了更好让用户配置Bean,必然会引入不同方式来配置Bean? 这便是xml配置,Java配置,注解配置等支持
- Spring 框架既然接管了Bean的生成,必然需要管理整个Bean的生命周期等;
- 应用程序代码从Ioc Container中获取依赖的Bean,注入到应用程序中,这个过程叫 依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI) ; 所以说控制反转是通过依赖注入实现的,其实它们是同一个概念的不同角度描述。通俗来说就是IoC是设计思想,DI是实现方式
- 在依赖注入时,有哪些方式呢?这就是构造器方式,@Autowired, @Resource, @Qualifier… 同时Bean之间存在依赖(可能存在先后顺序问题,以及循环依赖问题等)
需求二
通过面向切面(AOP)实现非侵入式的日志方法。
如果没有Spring框架,我们需要在每个service的方法中都添加记录日志的方法,比如:
/**
* find user list.
*
* @return user list
*/
public List<User> findUserList() {
System.out.println("execute method findUserList");
return this.userDao.findUserList();
}有了Spring框架,通过@Aspect注解 定义了切面,这个切面中定义了拦截所有service中的方法,并记录日志; 可以明显看到,框架将日志记录和业务需求的代码解耦了,不再是侵入式的了
/**
* aspect for every methods under service package.
*/
@Around("execution(* tech.pdai.springframework.service.*.*(..))")
public Object businessService(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// get attribute through annotation
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
System.out.println("execute method: " + method.getName());
// continue to process
return pjp.proceed();
}更进一步,你便能理解为何会有如下的知识点了:
- Spring 框架通过定义切面, 通过拦截切点实现了不同业务模块的解耦,这个就叫面向切面编程 - Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP)
- 为什么@Aspect注解使用的是aspectj的jar包呢?这就引出了Aspect4J和Spring AOP的历史渊源,只有理解了Aspect4J和Spring的渊源才能理解有些注解上的兼容设计
- 如何支持更多拦截方式来实现解耦, 以满足更多场景需求呢? 这就是@Around, @Pointcut… 等的设计
- 那么Spring框架又是如何实现AOP的呢? 这就引入代理技术,分静态代理和动态代理,动态代理又包含JDK代理和CGLIB代理等
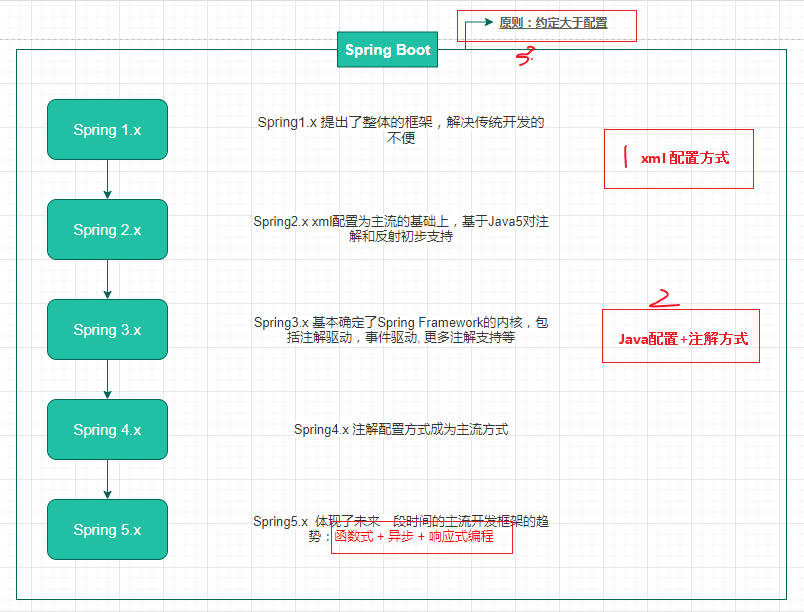
SpringBoot托管配置
Springboot实际上通过约定大于配置的方式,使用xx-starter统一的对Bean进行默认初始化,用户只需要很少的配置就可以进行开发了。
这个因为很多开发者都是从SpringBoot开始着手开发的,所以这个比较好理解。我们需要的是将知识点都串联起来,构筑认知体系。
结合Spring历史版本和SpringBoot看发展,最后结合Spring历史版本总结下它的发展: